(VOVWORLD) - In last week’s Digital life, we talked about the
data security risks posed by passwords and the current trend of passwordless authentication in Vietnam. This week we’ll continue our discussion of authentication that doesn’t require a password with Trinh Xuan Dat, an IT expert with
MSIG Insurance Vietnam, a subsidiary of Japan’s Mitsui Sumitomo Insurance Company.
 (Photo: delinea.com) (Photo: delinea.com)
|
Bao Tram: Could you elaborate the concept of passwordless authentication?
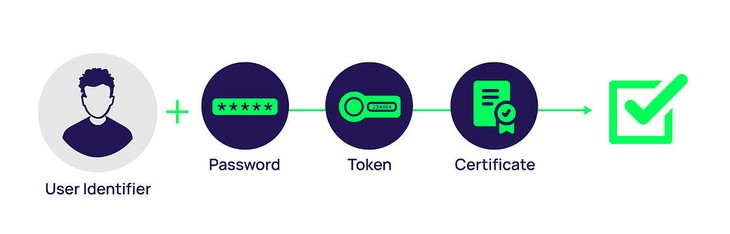
Xuan Dat: Passwordless authentication is a method that allows a user to gain access to an application or IT system without entering a password or answering security questions. Instead, the user provides some other form of evidence such as a fingerprint, proximity badge, or hardware token code. Passwordless authentication is often used in conjunction with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Single Sign-On solutions to improve the user experience, strengthen security, and reduce IT operations expense and complexity.
Bao Tram: What are the benefits of passwordless authentication for individuals and organizations?
Xuan Dat: Passwordless authentication strengthens security by eliminating risky password management practices and reducing attack vectors. It also improves the user experience by eliminating password and secrets fatigue. With passwordless authentication, there are no passwords to memorize or security question answers to remember. Users can conveniently and securely access applications and services using other authentication methods such as proximity badges, physical tokens, or USB devices. Users can use software tokens or digital certificates, biometric factors like fingerprint, voice, or facial recognition, or retina scanning, or a mobile phone application.
 (Photo: delinea.com) (Photo: delinea.com)
|
Bao Tram: Tell us how authentication that does not require a password works.
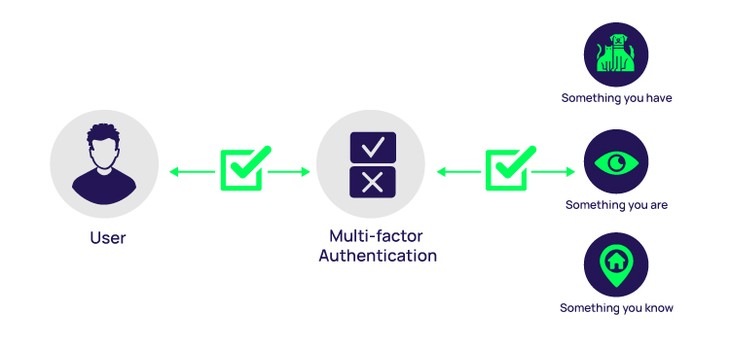
Xuan Dat: Passwordless authentication is typically deployed in conjunction with Single Sign-On, so a user can use the same proximity badge, security token, or mobile app to access all their enterprise applications and services. Passwordless authentication is also often used as part of an MFA solution, where users are forced to provide multiple forms of evidence to gain access to enterprise applications and systems. For example, to access a mobile phone app, a user might be required to tap a fingerprint sensor and enter a one-time, short-lived SMS code sent to their phone. Passwordless authentication provides a variety of functional and business benefits. It helps organizations improve the user experience, strengthen security, and simplify IT operations.
Bao Tram: How is it implemented in Vietnam? What are the difficulties?
Xuan Dat: In Vietnam, passwordless authentication is not something very new. A number of businesses have begun to apply the solution. For example, businesses that use the Microsoft Windows operating system - Windows 10 or 11 - can configure so that users use the Microsoft authenticator app, Windows Hello, to sign in to the enterprise’s computer network, apps, and services without the use of a password. Businesses that use Microsoft 365 can have users use mobile apps or digital certificates to log into the system. But we should remember that passwordless authentication means that we will have to use external factors, for example, SMS messages, token devices, or cards. The use of such external factors will force businesses and organizations to manage those devices, so they will need to consider the costs, users’ habits, and their capacity to deploy the solution.
Bao Tram: Thank you, Mr. Trinh Xuan Dat, IT expert with MSIG Insurance Vietnam, a subsidiary of Japan’s Mitsui Sumitomo Insurance Company, for granting VOV this interview.
Xuan Dat: Thank you.