(VOVWORLD) - The COVID-19 Delta variant, first identified in India, has already been detected in 96 countries, 11 more than last week, the World Health Organization (WHO) said in its weekly epidemiological update on Thursday.
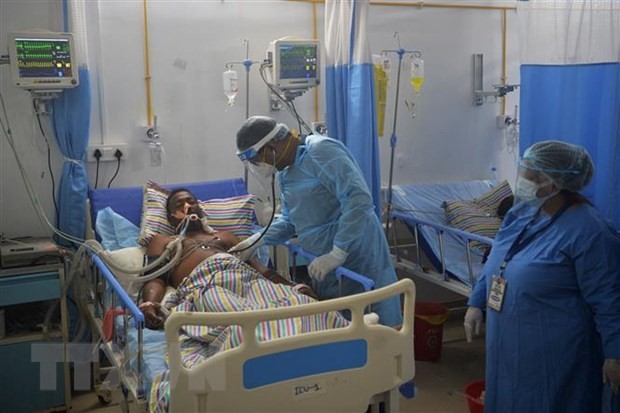 A COVID-19 patient in West Bengal, India, is hospitalized on June 1, 2021. (Photo: AFP/VNA) A COVID-19 patient in West Bengal, India, is hospitalized on June 1, 2021. (Photo: AFP/VNA) |
The Delta variant, also known as a “double mutant” because it carries two mutations, is 55% more transmissible than the Alpha variant (initially detected in the United Kingdom) and will rapidly become the dominant strain of coronavirus globally, said the WHO.
Africa has reported many new outbreaks of the variant in Tunisia, Mozambique, Uganda, Nigeria and Malawi. The continent has witnessed a "sharp increase" in new cases and deaths, according to the update.
First detected in October, 2020, the Delta variant is the latest threat hindering the COVID-19 fight globally. The WHO has categorized the Delta variant as a variant of concern in addition to the Alpha, Beta (first detected in South Africa), and Gamma (first found in Brazil).